dnf is a package management tool used for RPM-based Linux distributions like Fedora, Red Hat, CentOS, AlmaLinux, Rocky Linux, and others. In this article, we will show the useful dnf commands that allow us to list installed packages.
Listing Installed Packages
Example 1. List all installed packages with dnf command:
$ dnf list installed
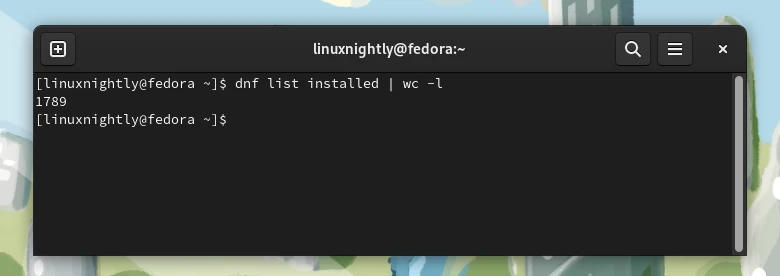
Example 2. To check the total number of installed packages, we can pipe the output to the wc command:
$ dnf list installed | wc -l
Example 3. List recently added packages (packages installed within the past week):
$ dnf list recent
List Available Packages
Example 1. To see a list of all the packages that can be downloaded and installed on your system:
$ dnf list available
Warning: you will get thousands of lines of output.
Example 2. To list all of the installed and available packages for your system:
$ dnf list all
Search For a Package
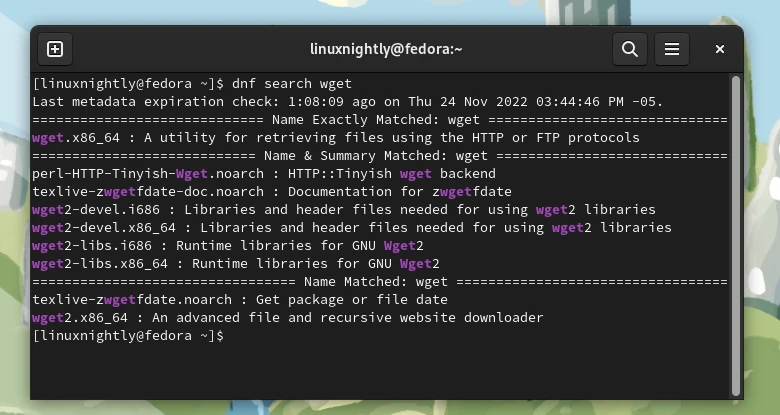
Example 1. To search for a package, execute the following command:
$ dnf search package_name
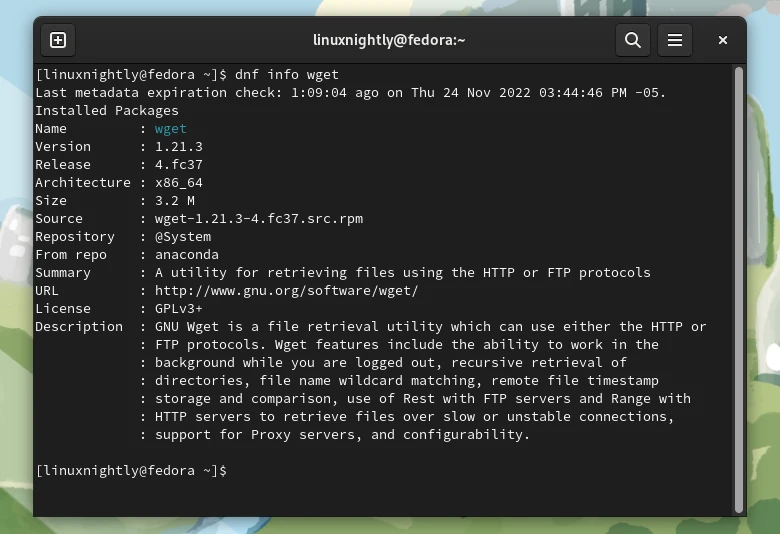
Example 2. To show information for a particular package:
$ dnf info package_name
Listing Package Groups
Linux distributions will often group multiple packages together, so the user doesn’t need to install many separate packages and can simply install them all with one group.
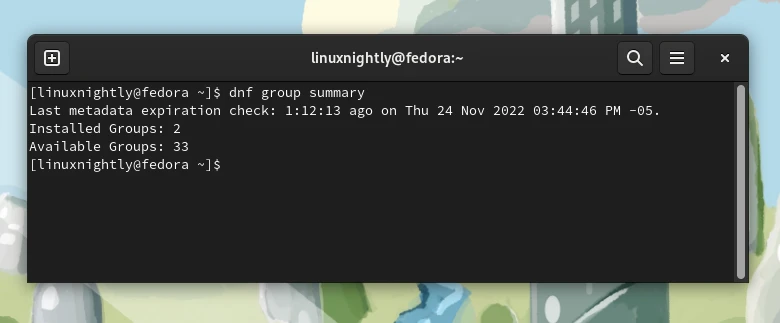
Example 1. You can use the summary flag see the total number of installed package groups, and the total number available:
$ dnf groups summary
Example 2. To get a list of package groups that are installed and available for installation:
$ dnf group list
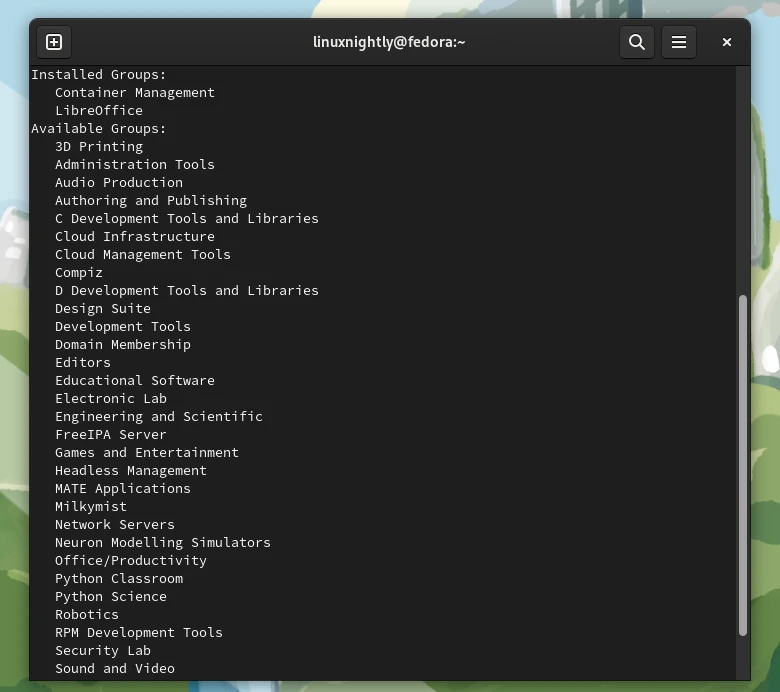
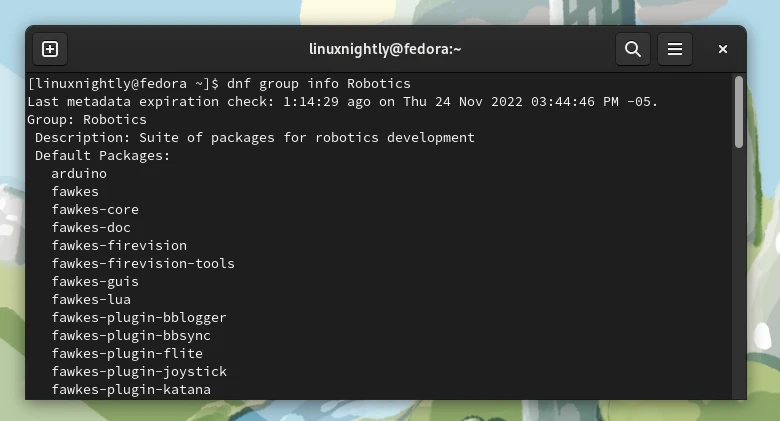
Example 3. We can see more information about a certain package group. To show information of the package group Robotics:
$ dnf group info Robotics
Listing Repositories
Example 1. To list all the repositories:
$ dnf repolist all
Example 2. If you want to only list the enabled repositories:
$ dnf repolist
To check more information about the dnf package manager:
$ dnf help

