This guide will show how to upgrade to Debian 11 Bullseye, which is the latest version of the operating system, released on August 14, 2021.
Upgrade to Debian 11 Bullseye
Step 1. You’ll need a completely up to date system in order to start the upgrade. Open a terminal and type the following commands to update all the packages on your Debian system.
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt full-upgrade
Step 2. You can also remove any unused dependencies to free up disk space before the upgrade.
$ sudo apt autoremove
Step 3. Next, we will need to edit the /etc/apt/sources.list file with the repository links for the latest version of Debian.
The following command will replace all instances of buster with bullseye.
$ sed -i 's/buster/bullseye/g' /etc/apt/sources.list
Step 4. When upgrading from Debian 10 to Debian 11, running the above command won’t be quite enough. You will also need to manually replace buster/updates on the debian-security line with bullseye-security, as the syntax has changed in the most recent release.
When you’re all done, your file will look like this:
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian/ bullseye main deb-src http://deb.debian.org/debian/ bullseye main deb https://security.debian.org/debian-security bullseye-security main deb-src http://security.debian.org/debian-security bullseye-security main # bullseye-updates, previously known as 'volatile' deb http://deb.debian.org/debian/ bullseye-updates main deb-src http://deb.debian.org/debian/ bullseye-updates main
Step 5. Once your sources.list file has the changes shown above, we can start the upgrade to Debian 11 Bullseye. It’s important to only do a partial upgrade at first.
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt upgrade
During the upgrade process, a prompt will ask you if you want to automatically restart services during the upgrade process. Be sure to select the “yes” option.
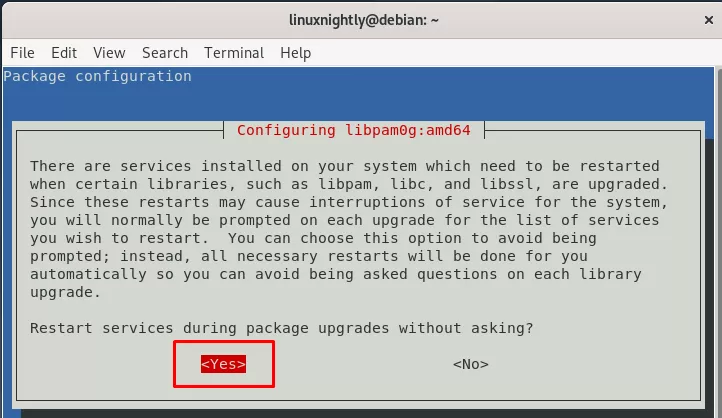
Step 6. Once the partial upgrade completes, you can run the apt full-upgrade command to complete the upgrade to Debian 11.
$ sudo apt full-upgrade
Step 7. For all the changes to take effect, reboot your system when the packages have finished installing.
$ sudo reboot
Step 8. When you boot back into Debian, you will be using the new Debian 11 Bullseye. You can run the hostnamectl command to see what version of Debian you’re running.
$ hostnamectl
Static hostname: linuxnightly
Icon name: computer-vm
Chassis: vm
Machine ID: 37eaf1edf1864dee9cfa90373206a449
Boot ID: 85b48f56f202422dbd2d6abc2f636c94
Virtualization: oracle
Operating System: Debian GNU/Linux 11 (bullseye)
Kernel: Linux 5.10.0-9-amd64
Architecture: x86-64


You are the best !! … Thank you for sharing … and thank you to Debian, it just works like a charm !!!!!!!! 🙂 🙂 🙂 🙂 🙂 🙂 🙂 🙂 🙂 🙂